We saw what the purpose of a Servlet Container and a Web server is, in the previous chapter. In this chapter, we are going to look at how a Servlet code would look like.
So, lets get started!!!
Servlet Skeleton
If I ask you, what are the components of a Java class, you’ll happily tell me that, there are first package statements and then imports and then the class declaration. Within the
Showing posts with label Servlets. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Servlets. Show all posts
Java J2EE Spring Chapter 2: Web Servers and Servlet Containers
In the previous chapter we looked at the history of the Web (Internet) and how JSPs and Servlets came into being. As you might have already guessed by now, any J2EE application needs a server on which it runs. It is called a Web Server. Also, the Servlet needs something in which it would run (Think of the JVM in which all java applications run) and that is called the Servlet container.
In this
In this
Java J2EE Spring Chapter 1: Servlet & JSP History
Here we are, studying for the SCWCD exam. I would like to congratulate you again for this decision of yours because of which you are going to get yourself SCWCD certified. It's a big step and am gonna be with you step by step to help you get this certification.
Well, it wouldn't be much fun preparing for a certification on JSPs and Servlets without knowing their history. Would it?
This
Well, it wouldn't be much fun preparing for a certification on JSPs and Servlets without knowing their history. Would it?
This
Spring Framework Session Tracking Example in Servlets
Here is a simple session tracking example in servlets using Tomcat, our pretty pet. We are familiar with using cookies in servlets because we've already done an example and you should note that there are some drawbacks of cookies. One of the major drawbacks that strikes to your mind is they may not stored. Yes
What if cookies are not stored by the browser?
A. Session tracking to the rescue!
A session refers to all the requests made by a user to a web application. This session is unique for every user and is stored in the server itself. For every session, the default lifetime is 20 minutes which can be changed.
An ID will be generated which is usually look like this 4BABD9D86DFF9061DDC3DA4C8A9E2498 (this is just an example) which is unique and random. This is usually stored in a cookie or in some invisible input field, however the session is maintained by the web server.
We need to track all the user's requests made for a particular application, this phenomenon is called as Session Tracking. All the regarded information i.e. the track of user's requests is stored in the web server itself.
That's it. In this way we can work out with session tracking in servlets. Simple is that. Also see Cookies example in servlets
What if cookies are not stored by the browser?
A. Session tracking to the rescue!
A session refers to all the requests made by a user to a web application. This session is unique for every user and is stored in the server itself. For every session, the default lifetime is 20 minutes which can be changed.
An ID will be generated which is usually look like this 4BABD9D86DFF9061DDC3DA4C8A9E2498 (this is just an example) which is unique and random. This is usually stored in a cookie or in some invisible input field, however the session is maintained by the web server.
We need to track all the user's requests made for a particular application, this phenomenon is called as Session Tracking. All the regarded information i.e. the track of user's requests is stored in the web server itself.
Folder structure
Project path: D:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0\webapps\sessiont
Project structure
sessiont
|_ index.html
|_ WEB-INF
|_ web.xml
|_ classes
|_ SessionExample.java
|_ SessionExample.class
|_ PrintAttribute.java
|_ PrintAttribute.class HTML File(s)
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Get a Hai for me</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/sessiont/mt" method="get">
<input type="text" name="user"/>
<input type="submit" value="Get"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Deployment Descriptor - web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>myser</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>SessionExample</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>myser</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/mt</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>myser1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>PrintAttribute</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>myser1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/rd</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Servlet Programs
SessionExample.java
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class SessionExample extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest
req,HttpServletResponse res)throws ServletException,IOException
{
String st=req.getParameter("user");
HttpSession ses=req.getSession();
ses.setAttribute("uname",st);
res.sendRedirect(res.encodeURL("/sessiont/rd"));
}
}PrintAttribute.java
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PrintAttribute extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res)throws ServletException,IOException
{
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
HttpSession ses=req.getSession();
String st=(String)ses.getAttribute("uname");
pw.println("<h1> Hai "+st+"</h1>");
}
}Output
The following screenshots show you sample output of this application.
Explanation
index.html
The HTML file consists of two input fields, one of type text and the other one of type SUBMIT. The name of the text type input field is user. Whenever user hits enter or click on the submit button, the form is submitted to the web server to the url http://localhost:8080/sessiont/mt and then the class associated with this URL is SessionExample.java. This get's executed.
web.xml
There is nothing to say about
web.xml, it is understood and it's obvious. /mt URL is associated with SessionExample and /rd with PrintAttribute classes.SessionExample.java
HttpSession ses=req.getSession(); The getSession() method in HttpServletRequest class get's the session associated with the request (if there is no session new one will be created). This method returns the javax.servlet.http.HttpSession object.ses.setAttribute("uname",st); The setAttribute() method takes a key value pair with uname as key (here) and st is the value. These attributes are very important and they carry the information. Here st contains the data that user has typed in the text field (input field of type text) with name as user. This is obtained from getParameter("user"); (see above).res.sendRedirect(res.encodeURL("/sessiont/rd")); The sendRedirect() method in HttpServletResponse takes a String which contains the URL to be redirected to. Here I made a method call to encodeURL() which is present in HttpServletResponse and takes String as parameter. This parameter is the URL to be encoded. By calling this method and sending the parameter you can observe the jsessionid in the URL (see it in the 2nd output image).PrintAttribute.java
HttpSession ses=req.getSession(): The same thing as explained above. But here, the Session is already created and now it is sent.String st=(String)ses.getAttribute("uname"); Here, the session is already created and now we can call getAttribute("uname") which returns the value of the uname.That's it. In this way we can work out with session tracking in servlets. Simple is that. Also see Cookies example in servlets
Labels:
Servlets
Spring Hibernate Display Current Date using GenericServlet
We have a class named Date from java.util.Date package. We can use the Date class methods to display the date. We are going to display this date in the webpage using servlets.
Here we are using init methods to initialize the names and values. with this we can get the names and values from the web.xml file while the program runs. Actually this init(javax.servlet.ServletConfig) method is invoked by the container during initialization phase of the servlet interface.
init() method is a convienience method provided in javax.servlet.GenericServlet class. Generally, it is suggested that init(javax.servlet.ServletConfig) method present in javax.servlet.GenericServlet class should be given a chance to get executed, during servlet's initialization. This method, apart from performing some initialization process, invokes init() method at the end.
Let us come to our Date application using servlet.Using Date calss create a new Date object 'd'. This date object contains the current date. But we can't display the object directly in the webpage. So convert the object to String using toString() method.Then display the date in the form of string in the servlet.
The Structure of our DateApp is :
web.xml
and tags. Based on this the logical name /firstwill be called by Servlet.
DateSrv.java
In the above web.xml we used urlpattern as '/first' so while running the program type the url-pattern given in web.xml in the addressbar of your browser.
Output:
Here we are using init methods to initialize the names and values. with this we can get the names and values from the web.xml file while the program runs. Actually this init(javax.servlet.ServletConfig) method is invoked by the container during initialization phase of the servlet interface.
init() method is a convienience method provided in javax.servlet.GenericServlet class. Generally, it is suggested that init(javax.servlet.ServletConfig) method present in javax.servlet.GenericServlet class should be given a chance to get executed, during servlet's initialization. This method, apart from performing some initialization process, invokes init() method at the end.
Let us come to our Date application using servlet.Using Date calss create a new Date object 'd'. This date object contains the current date. But we can't display the object directly in the webpage. So convert the object to String using toString() method.Then display the date in the form of string in the servlet.
The Structure of our DateApp is :
Date d=new Date();Use setContentType() method to display in text/html format in the java file of servlet.
String s=d.toString();
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>in the above web.xml the mappings are done based on serletname 'ABC'.We can give any name but it should be same in
<!DOCTYPE web-app
PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd">
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ABC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>blog.javabynataraj.DateSrv</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>sno</param-name>
<param-value>1001</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>sname</param-name>
<param-value>sharukh</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ABC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/first</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
DateSrv.java
package blog.javabynataraj;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class DateSrv extends GenericServlet
{
public void service(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)throws ServletException,IOException
{
ServletConfig cg=getServletConfig();
String s1=cg.getInitParameter("sno");
String s2=cg.getInitParameter("sname");
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
res.setContentType("text/html");
Date d=new Date();
String s=d.toString();
pw.println("<b> Date is"+s +"</b>");
pw.println("<font color=red ><br> Param1 :"+s1+"<br> param2 is: "+s2+"</font>");
pw.close();
}//service
}//class
In the above web.xml we used urlpattern as '/first' so while running the program type the url-pattern given in web.xml in the addressbar of your browser.
Output:
Download the above Application in jar file.
J2EE Spring Hibernate 1.Web application introduction.
WebApplication is a collection of web resources like HTML files, JavaScript files, image files Servlets, jsps and etc.

In order to make resources of a application as globally accessible resources developed as web resources of web-application each web-resource develops one webpage and this webpage is globally accessible page.
The web-application that is moved to internet network after development is called Website.
A web application contains two types of web-resources.
EX: HTML,JavaScript programs.
The web-resource program that executed in the server(web-server/application server)is called server-side web-resource program.
EX : Servlet,JSP

In order to make resources of a application as globally accessible resources developed as web resources of web-application each web-resource develops one webpage and this webpage is globally accessible page.
The web-application that is moved to internet network after development is called Website.
A web application contains two types of web-resources.
** Server side Web-resource
** Client side Web-resource
EX: HTML,JavaScript programs.
The web-resource program that executed in the server(web-server/application server)is called server-side web-resource program.
EX : Servlet,JSP
- Don't decide weather web-server program is server-side or client side based on the place where it resides and decide based on the place where it executes.
Spring Framework Handling Choice in HTML form in Servlets
The following illustrates handling choice in HTML form in Servlets. Till now we have seen working with data in the text box now let us see how to work out with the drop downs. A drop down or a choice looks like this.
Here are all the files..
Here are all the files..
Folder structure
Project folder: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0\webapps
selectser
|_ index.html
|_ WEB-INF
|_ web.xml
|_ classes
|_ SelectExample.java
|_ SelectExample.class
HTML File(s)
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Select a language</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/selectser/ss" method="post">
<select name="lang">
<option value="C">C</option>
<option value="C++">C++</option>
<option value="Java">Java</option>
<option value="Python">Python</option>
</select>
<input type="submit" value="SUBMIT"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>Deployment Descriptor - web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>sser</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>SelectExample</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>sser</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ss</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Servlet Programs
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class SelectExample extends HttpServlet
{
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
// Get value first
String val=req.getParameter("lang");
// Get writer from res
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h1> You selected "+val+"</h1>");
}
}Working? Let's see.
The following output shows that it is working.
 |
| The HTML form |
 |
| Print what is selected |
Explaining things..
index.html
<select name="lang"> The <select> does it all. It encloses a set of options to be selected. It has a name which can be used to retrieve which option is selected.<option value="C">C</option> The <option> defines an item in the drop down. The value of this is returned when we call the getParameter("lang") provided this option is selected and submitted. Here value is for the programmers to get and the name that is enclosed between the opening and closing of the option tag is for the user to see.web.xml
<url-pattern>/ss</url-pattern> This is the url pattern. The tomcat observes this and invokes the class associated with it.<servlet-class>SelectExample</servlet-class> SelectExample is the class associated with the above pattern.SelectExample.java
String val=req.getParameter("lang"); Get the value of the option that is submitted. Here i have used the lang which is the name you have encountered above. When this is passed, we get the value of the option that is selected.PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter(); Get the PrintWriter object to write something on the dynamic page for the user.pw.println("<h1> You selected "+val+"</h1>"); Print the value the user has selected in a <h1> tag.In this way we can handle a drop down (choice) in HTML form in Servlets. Hope this helps. Feel free to drop a comment.
Labels:
Servlets
Java J2EE Spring What is the difference between doGet() and doPost() methods ?
The difference has given below......
doGet | doPost |
In doGet Method the parameters are appended to the URL and sent along with header information | In doPost parameters are sent in separate line in the body |
Maximum size of data that can be sent using doget is 240 bytes | There is no maximum size for data |
Parameters are not encrypted | Parameters are encrypted |
DoGet method generally is used to query or to get some information from the server | DoPost is slower compared to doGet since doPost does not write the content length |
DoGet should be idempotent. i.e. doget should be able to be repeated safely many times | This method does not need to be idempotent. Operations requested through POST can have side effects for which the user can be held accountable for example updating stored data or buying items online. |
DoGet should be safe without any side effects for which user is held responsible. | This method does not need to be either safe. |
Labels:
Differences,
java,
Servlets
Spring Framework Cookies in Servlets with Example
The following tutorial brings you an understanding of how-to use cookies in Java servlets, one of the interesting and important concepts to go around. In this post, i'll explain about cookies pragmatically for a better understand. All complete files of the application along with folder structure are discussed.
In my PC, Tomcat is installed in the port 8080 and i will access it as, the project name is cookies i will type the same URL in the address bar of my favorite browser.
Folder Structure
Webapps folder: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0\webapps
Project structure
cookies
|_ index.html
|_ WEB-INF
|_ web.xml
|_ classes
|_ CookieExample.java
|_ CookieExample.class
|_ GetCookie.java
|_ GetCookie.class
HTML Files
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Cookies Example in Servlets</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=wheat>
<center>
<h1>Cookies Example in Java</h1>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/cookies/co" method="Post">
First name: <input type="text" name="fname">
Last name: <input type="text" name="lname">
<input type="submit"value="SUBMIT">
</form>
</center>
</body>
</html>Deployment Descriptor
web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mys</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>CookieExample</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mys</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/co</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mls</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>GetCookie</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mls</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/st</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Servlet Programs
CookieExample.java
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class CookieExample extends HttpServlet
{
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
String fname=req.getParameter("fname");
String lname=req.getParameter("lname");
Cookie f=new Cookie("first_name",fname);
Cookie l=new Cookie("last_name",lname);
res.addCookie(f);
res.addCookie(l);
res.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/cookies/st");
}
}GetCookie.java
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class GetCookie extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h1>");
Cookie[] c=req.getCookies();
for(Cookie k:c)
{
pw.println(k.getValue());
}
pw.println("</h1>");
}
}Working? Yes it works.
Invoke the Tomcat at the port installed in your PC or if you are accessing it from another PC, probably then, tomcat installed in that PC. Write the programs, create folders in accordance with the given structure and there will be what you want. Don't forget to compile the classes!!
In my PC, Tomcat is installed in the port 8080 and i will access it as, the project name is cookies i will type the same URL in the address bar of my favorite browser.
http://localhost:8080/cookies
As the default file is index.html the above URL will suffice to load the index.html file, an addition of /index.html is not necessary at the end.
You'll see the following output.
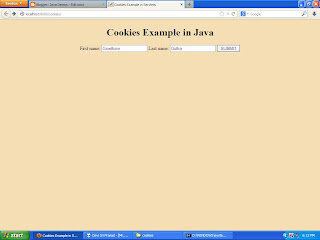 |
| index.html file in Firefox |
Click on the SUBMIT then,
 |
| Output produced by GetCookie class |
Let me explain
The HTML file
The html file is as usual, a very normal HTML file you might undergo when working out with most servlet programs. The HTML file here consists of input fields with names fname and lname which are used to get the values in them. The other input field is a SUBMIT button which submits the HTML form to the url specified in the <form> tag. The type of method i used here is post.
The web.xml
web.xml file contains two <servlet> and <servlet-mapping> tags (importantly) which are written for two classes. One is the main class i.e. the class that gets the request made by the user, i.e. the data sent by the user can be caught be this servlet. Another class is GetCookie which is a class that gets the cookies stored by the previous servlet.
Servlet Programs
CookieExample.java
req.getParameter("fname") and req.getParameter("lname"): These methods take in the name of the input field and return the value in them. The values are stored in fname and lname respectively.
Cookie f=new Cookie("first_name", fname): This is the constructor of the javax.servlet.http.Cookie takes in a name (the name of the cookie) and value (value to set in the cookie). The other method is also the same but stores a different value under a different name.
res.addCookie(f), res.addCookie(l): Creating a cookie isn't enough. You'll have to set them in the client's web browser so are these methods.
res.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/cookies/st"): Redirect to the specified URL. This URL is associated with GetCookie class (refer web.xml). You can also simply write /cookies/st instead of such lengthy URL.
What is a cookie?
A cookie is a name-value pair which is stored in a user's browser for the sake of the user by the web server when the servlet program says to do so.
GetCookie.java
Here i am writing doGet() because in the above servlet, sendRedirect() method is called stating to redirect to the URL pattern associated with GetCookie. It is a doGet() call in fact.
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter(): The java.io.PrintWriter class is used to write (print) something on the dynamic page that is generated. To get a PrintWriter object we need to call the getWriter() method present in the HttpServletResponse.
pw.println("<h1>"): Open the <h1> tag.
Cookie[] c=req.getCookies(): To get cookies stored by this application we need to call the getCookies() method present in the HttpServletRequest class. This gives an array of cookies (Cookie[]).
pw.println(k.getValue()): Get value stored in each cookie and print them. The for-each loop is explained by me before.
pw.println("</h1>"): Close the <h1> tag.
Labels:
Servlets
Java J2EE Spring Difference between ServletContext and ServletConfig ?
What is the Difference between ServletConfig and ServletContext.?
ServletConfig:
public interface ServletConfig
ServletConfig encapsulates servlet configuration and gives access to the application (servlet context) object. Servlet initialization parameters appear in the servlet configuration file. Each servlet class may have several different servlet instances, one for each servlet parameters:
Example:
ServletContext:
public interface ServletContext
ServletContexts encapsulate applications. Applications are generalized virtual hosts; a URL prefix defines a distinct application. So /myapp and /yourapp could define different applications. As a degenerate case, each virtual host has its own ServletContext.
Example:
ServletConfig:
public interface ServletConfig
ServletConfig encapsulates servlet configuration and gives access to the application (servlet context) object. Servlet initialization parameters appear in the servlet configuration file. Each servlet class may have several different servlet instances, one for each servlet parameters:
- One ServletConfig per servlet
- It is used to pass deploy-time info to servlet and configured in the deployment descriptor file.
- it is used to access ServletContext
- It is within the Servlet element in Deployment descriptor.
- It is accessed by using getServletConfig().getInitParameter("myname");
- It is available only to the servlet in which init-param is configured.
Example:
ServletContext:
public interface ServletContext
ServletContexts encapsulate applications. Applications are generalized virtual hosts; a URL prefix defines a distinct application. So /myapp and /yourapp could define different applications. As a degenerate case, each virtual host has its own ServletContext.
- It returns the current context of a web application running in a particular JVM..
- If the web application is distributed,it is one per JVM.
- It is used to access the elements configured in deployment descriptor.
- It is accessed by using getServletContext().getInitParameter("myname");
It is available to any servlet or jsp that is part of web application.
Example:
Spring Framework Pre Check web.xml for Errors in Servlets
Sometimes we might be disgusted when we encounter errors related to web.xml while executing our web application, we might not understand it at times even when we look at the Tomcat logs. So in this post i'll discuss about how to pre check the web.xml for errors.
As web.xml is an xml file, the default application for xml files is Internet Explorer, so open web.xml in Internet Explorer. That's it.
See following, i had intentionally written an error in web.xml (not properly closing the
When i open this in Internet Explorer, the screenshot will look like..
When i write it correctly, closing the tag properly, it will look like..
Unlike the previous screenshot, in this screenshot you have the web.xml correctly displayed which means that the xml file is well parsed with no errors.
However, errors that are not related to the syntax such as change servlet name in tags i.e. different servlet names in servlet-mapping and servlet tags cannot be identified unless you are familiar with.
This is just a tip that helps you detect xml parsing related errors. Hope this helps.
As web.xml is an xml file, the default application for xml files is Internet Explorer, so open web.xml in Internet Explorer. That's it.
See following, i had intentionally written an error in web.xml (not properly closing the
<web-app>.
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mys</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>CookieExample</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mys</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/co</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<web-app>
When i open this in Internet Explorer, the screenshot will look like..
 |
| web.xml error in Internet Explorer |
When i write it correctly, closing the tag properly, it will look like..
 |
| web.xml is displayed in Internet Explorer |
Unlike the previous screenshot, in this screenshot you have the web.xml correctly displayed which means that the xml file is well parsed with no errors.
However, errors that are not related to the syntax such as change servlet name in tags i.e. different servlet names in servlet-mapping and servlet tags cannot be identified unless you are familiar with.
This is just a tip that helps you detect xml parsing related errors. Hope this helps.
Spring Hibernate Servlet - Servlet Communication
Servlet - Servlet Communication
Communication between Java servlets is called as Servlet communication. It is nothing but, sending users request and the response object passed to a servlet to another servlet. You may ask, what is the use of passing these objects. Well, i have an answer. As seen in the servlet examples written till date, one common method we are using, getParameter(), used to get the user input value in a specified field. So, when a request object is passed from one servlet to another servlet, then you can use this method to get the input that the user has given in a HTML/JSP form. Following example, gives better understand of what is said now.
Servlet Communication - Folder Structure
webapps
|_ servletcom
|_ index.html
|_ WEB-INF
|_ web.xml
|_ classes
|_ FirstServlet.java
|_ FirstServlet.class
|_ FinalServlet.java
|_ FinalServlet.class
Servlet Communication - index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Servlet-Servlet Communication</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/servletcom/pass" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="uname" width="20" />
Password: <input type="password" name="pass" width="20" />
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Login" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
action="/servletcom/pass": /pass is the url pattern in web.xml and the servletcom is the name of the project (folder name). The project folder name must be specified here for sure, else the statement means to search in the webapps directory but not within the project.
method="post": Invisible submission, at the background.
name="uname": Used to get the value in this field in Servlet class.
name="pass": Used to get the value in this field in Servlet class.
Servlet Communication - web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>comservlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>FirstServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>comservlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/pass</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>lservlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>FinalServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>lservlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/we</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Here i wrote 2 classes, for servlet communication, as /pass is the url pattern pointing that the corresponding action controlling class is FirstServlet, and also, the user's data sent to this url pattern, FirstServlet will be called first by the servlet container. Next one, /we, when servlet container gets request to the url-pattern /we, the FinalServlet class will be invoked.
For better understand, See Understanding web.xml in Java Servlets
Servlet Communication - FirstServlet.java
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.*;
public class FirstServlet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
String uname=req.getParameter("uname");
String pass=req.getParameter("pass");
getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/we").forward(req,res);
}
}
getServletContext(): Gets the ServletContext object. ServletContext is an interface, and may be an implementation class of ServletContext is written and it's object is sent. ServletContext is created by the Servlet Container (Tomcat here) and by using this method we will call it. This object contains common data for the entire web application, so reusable and also helps in communicating with the servlet container because it was generated by the Servlet Container (could also be one of the reason).
getRequestDispatcher(): This is a method of the ServletContext interface.This returns RequestDispatcher object which is again an interface and may be some implementation class is written and its object is sent (to us). The purpose of this method is to pass the request to another servlet. It takes String as parameter, which is the url-pattern pointing the servlet that we are going to send the request to (here FinalServlet).
forward(req,res): This is a method in RequestDispatcher interface, that helps us to forward user's request to another servlet (the servlet that the RequestDispatcher object points out to) (FinalServlet here).
Servlet Communication - FinalServlet.java
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.*;
public class FinalServlet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
String uname=req.getParameter("uname");
String pass=req.getParameter("pass");
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h1>Your username is "+uname+"</h1>");
pw.println("<h1>Your password is "+pass+"</h1>");
}
}
javax.servlet.http.*: Contains HttpServlet, HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponseclasses (used here).
javax.servlet.*: Contains ServletException (used here).
java.io.*: Contains PrintWriter, IOException (used here).
pw.println("<h1>Your username is "+uname+"</h1>"): Present in the PrintWriter class, prints username (the value that user gives in field named uname).
pw.println("<h1>Your password is "+pass+"</h1>"): Present in the PrintWriter class, prints password (the value that user gives in field named pass).
Note: The req,res objects are given by the FirstServlet.java and those are used here. These objects are passed from FirstServlet.java to FinalServlet.java by Servlet container (Tomcat here).
Another Note: Do not forget to compile the class and re/start tomcat! ;)
Labels:
Servlets
Spring Hibernate doPost() in doGet() in Java Servlets - What's the difference?
doPost() in doGet() in Servlets
Till now we have seen working with doPost() and doGet(). Now let us see how to write doPost() in doGet() before that lets us talk about them for some time. doPost() does invisible data submission whereas doGet() does visible data submission, through url. While doGet() is not recommended for everything, doPost() is used to carry passwords. But some tricky people, tries to pass data through url, though doPost() was to be done. However, this doesn't happen unless they use some extension like Tamper Data. To give them (only the people who thinks of doing so), you can write doPost() within doGet(). Let us look at the example for a better understand.
doPost() in doGet() - Folder Structure
webapps
|_ dopostindoget
|_ WEB-INF
| |_ classes
| | |_ doPostIndoGet.java
| | |_ doPostIndoGet.class
| |_ web.xml
|_ index.html
doPost() in doGet() - index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>doPost in doGet</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/dopostindoget/dpdg" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="uname" width="20" />
Password: <input type="password" name="pass" width="20" />
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Login" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
form: User input is taken in a form containing input fields.
action="/postservlet/ps": /ps is the url pattern in web.xml and the postservlet is the name of the project (folder name). The project folder name must be specified here for sure, else the statement means to search in the webapps directory but not within the project.
method="post": Invisible submission, at the background.
name="uname": Used to get the value in this field in Servlet class.
name="pass": Used to get the value in this field in Servlet class.
doPost() in doGet() - web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>testservlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>doPostIndoGet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>testservlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/dpdg</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Cant understand web.xml? See Understanding web.xml in Java Servlets
doPostIndoGet.java
 |
| doPostIndoGet Result |
 |
| doPostIndoGet Tricked. See Address Bar. |
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.*;
public class doPostIndoGet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
doPost(req,res);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
String user=req.getParameter("uname");
String password=req.getParameter("pass");
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h1> Welcome "+user+"</h1> <br/>");
pw.println("<h2> Your Password is "+password+"</h2>");
}
}
javax.servlet.http.*: Contains HttpServlet, HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponseclasses (used here).
javax.servlet.*: Contains ServletException (used here).
java.io.*: Contains PrintWriter, IOException (used here).
doGet(): To let the tricky people, submit through address bar also. Passing, req,res objects to doPost(), if doPost() was just written without doGet(), then tricky people couldn't pass it through address bar. Observing the screenshot gives a better understand.
javax.servlet.*: Contains ServletException (used here).
java.io.*: Contains PrintWriter, IOException (used here).
doGet(): To let the tricky people, submit through address bar also. Passing, req,res objects to doPost(), if doPost() was just written without doGet(), then tricky people couldn't pass it through address bar. Observing the screenshot gives a better understand.
doPost(): For url type submission, submission through url, observe method="post" in index.html
PrintWriter: Part of the java.io package.
req.getParameter("uname"): Get the value (user input value) in the input field nameduname.
req.getParameter("pass"): Get the value (user input value) in the input field named pass.
pw.println("<h1>Welcome "+user+"</h1> <br/>"): Present in the PrintWriter class, write Welcome along with user within <h1> with a line break. (here).
pw.println("<h2> Your Password is "+password+"</h2>"): Display password withinh2 tag.
Note: Do not forget to compile the class and re/start tomcat! ;)
Note: Do not forget to compile the class and re/start tomcat! ;)
Labels:
Servlets
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Labels
.equals
= operator
abstract class
abstract method
abstract window toolkit
Access Modifiers
accessing java beans
accessing javabeans
action events
actionperformed
active
addition
Advanced
Advanced Overloading
AdvJavaBooks
Agile development
ajax
alive
AMQP
and
Android
anonymous class
anonymous inner class
Ant
ant tutorials
anti patterns
antipatterns
Apache Camel
api for jsp
api for servlet
api for servlets
api jsp
application context
application scope
application session
Apps
Architecture
are you eligible for the ocmjd certificaiton
are you eligible for the scjd certification
arithmetic operator
arpanet
array construction
array declaration
array initialization
array list
array to list conversion
arraylist
arraylist of strings
arraylist of types
arraylist questions
arraylists
Arrays
arrays in java
ask for help
assert
assert in java
assertions
assertions in java
assignment
assignment operator
Atlassian
attribute visibility
authentication
authorization
autoboxing
autounboxing
awt
AWT Event Handling
awt interview questions
AWT Layouts
awt questions
awt questions and answers
backed collection
backed collections
Basic
Basics of event handling
bean attributes
bean properties
bean scope
Beginner
best practices
BigData
blocked
books
boxing
buffer size
bufferedreader
bufferedwriter
business delegate
business delegate pattern
calendar
case statement
casting in java
casting interview questions
chapter review
choosing a java locking mechanism
choosing a locking mechanism
choosing a thread locking mechanism
class inside a method
class questions
class with no name
class without a name
classes interview questions
Clipboard
closing jsp tags
code snap
coding
cohesion
collection generics
collection interview questions
collection methods
collection of types
collection questions
collection searching
collection types
Collections
Collections Framework
collections interview questions
collections sorting
colors in java swings
colors in swing
command line arguments
communication between threads
comparable
comparator
comparison operators
compiling java classes
computers
concurrency example and tutorial
config
Configuration
ConnectionPooling
constructor creation
constructor interview questions
constructor overloading
constructors in java
containers
contents of deployment descriptor
contents of web.xml
context
context scope
converting array to list
converting list to array
core java
core java interview
core java interview question
core java interview questions
core java questions
core java;
core java; object oriented programming
CoreJava
CoreJavaBooks
CORS
coupling
create threads
creating 2 dimensional shapes
creating 2D shapes
creating a frame
creating a jframe
creating a thread
creating an arraylist
creating an inner class
creating an interface
creating java beans
creating java threads
creating javabeans
creating threads
creating threads in java
CSS
cURL
currency
current thread determination
custom tag library
custom taglib
custom taglibs
custom tags
CVS
dao
dao design pattern
dao factory pattern
dao pattern
data access object
data access object pattern
data structure and algorithm
database
date and time tutorial
date format
dateformat
dates
deadlock
deadlocks
debugging
Declarations
decorator pattern
decrement
default
deleting sessions
deploy web app
deployment
deployment descriptor
deployment descriptor contents
deployment of web application
deserialization
deserialize
design pattern
design pattern interview questions
design patterns
Designpatterns
destory method
destroy
destroying sessions
determining current thread
determining the current thread
Developer
Differences
different types of collections
display stuff in a frame
displaying images
displaying images in java swings
displaying images in swings
displaying text in a component
division
do while loop
doget
dohead
dopost
doput
DOS
Downloads
drawing a line
drawing an ellipse
drawing circles
drawing ellipses
drawing lines
Drools tutorial
eBooks
Eclipse
Eclipse Tutorial
Encapsulation
encapsulation in java
enhanced for loop
entity facade pattern
enumerations
enumerations in java
enums
equal to
equals
equals comparison
error and exception
error codes
error handling in servlets
error page
event handling in swings
event listeners
exam prep tips
example servlet
Examples
exception
exception handling
exception handling in servlets
exception handling interview questions
exception handling questions
Exceptions
exceptions in java
exceptions in web applications
explicit locking
explicit locking of objects
file
file navigation
filereader
filewriter
final class
final method
FireBug
first servlet
FIX protocol
FIX Protocol interview questions
FIX protocol tutorial
font
fonts
for each loop
for loop
form parameters
form values
formatting
forwarding requests
frame
frame creation
frame positioning
frame swings
front controller
front controller design pattern
front controller pattern
fundamental.Java
FXML
Games
garbage collection
garbage collection interview questions
garbage collection questions
garbage collector
gc
gc questions
general
generic
Generics
generics collections
Geo
get
get set methods
getattribute
getting bean property
getting form values
getting form values in servlet
getting scwcd certified
getting servlet initialization parameters
getting sun certified
Google
Graphics2D
gregorian calendar
handling strings in java
hash
hash map
hash table
hashcode
hashmap
hashset
hashtable
head
head request
HeadFirst
heap
heaps
hibernate
hibernate interview questions
hibernate interview questions and answers
hibernate questions
hibernate questions and answers
Hibernate Tutorial
HibernateBooks
homework
How To
HTML
HTML and JavaScript
html form
http request
http request handling
http request header
http request methods
http request servlet
http request type
http session
httprequest
httprequest methods
httpservlet
httpservlet interview questions
httpservlet interview questions with answers
httpsession
httpsession interview questions
httpsession questions
HttpSessionActivationListener
HttpSessionAttributeListener
HttpSessionBindingListener
if
if else
if else block
if else statement
Image IO
implementing an interface
Implicit objects
increment
info
inheritance
inheritance in java
init
init method
Initialization Blocks
inner class
inner class inside a method
inner classes
innerclass
installation
instanceof
instanceof operator
IntelliJ
interaction between threads
interface
interface interview
interface questions
interfaces
interfaces in java
interfaces interview questions
internet history
interrupting a thread
interrupting threads
Interview
interview questions
interview questions on design patterns
interview questions on exception handling
interview questions on java collections
interview questions on serialization
introduction to java threads
introduction to jsps
introduction to threading
introduction to threads
invalidating session
Investment Banking
IO Package
iscurrentthread
iterator
J2EE
j2ee api
j2ee design pattern
j2ee design pattern interview questions
j2ee design patterns
j2ee hibernate interview questions
j2ee history
j2ee interview
j2ee interview questions
j2ee mvc
j2ee mvc pattern
j2ee programmer
j2ee questions
j2ee servlet api
j2ee session
j2ee struts interview questions
java
java 5 tutorial
Java 8
java arrays
java assertions
java assignments
java awt questions
java bean
java bean scope
java beans
java beginners tutorial
Java career
java certification
Java Class
java collection interview questions and answers
java collection tutorial
java collections
java collections interview questions
java constructors
java currency
Java CV
java data base connectivity
java database connectivity
java database connectivity interview questions and answers
java dates
java design pattern
java design patterns
java developer certification
Java EE
java encapsulation
java enums
java event listeners
java exceptions
java formatting
java garbage collection
java garbage collector
java gc
java heap
Java I/O
java inheritance
java input output
Java Interface
Java Interview
Java Interview Answers
Java Interview Questions
Java Introduction
java io
java IO tutorial
java iterator
java jdbc
Java JSON tutorial
Java Key Areas
java lists
java literals
java locks nested
Java Media Framework
java methods
java multithreading
Java multithreading Tutorials
java nested locks
java networking tutorial
java numbers
Java Objects
java operators
java overloading
java parsing
Java Programming Tutorials
java race conditions
java regex
java regular expressions
Java resume
java scjp
java searching
java serialization
java server pages
java server pages api
java server pages questions
java spring interview questions. j2ee spring interview questions
java stack
java strings
java swing
java swing event listeners
java swing frame
java swing images
java swings
java swings images
java thread explicit locking
java thread lock scope
java thread locking
java thread locking mechanism
java thread locking objects
java threads
java threads race condition
java tips
java tokenizing
Java Tools
Java Tutorial
java ui questions
Java Utilities
java variables
java wrappers
Java xml tutorial
java.lang
java8
javabean
javabean accessing
javabean scope
JavaBeans
javac
JavaEE
JavaFX
JavaFX 3D
JavaFX 8
JavaOne
JavaScript
JavaTips
JDBC
jdbc driver
jdbc example
jdbc interview questions
jdbc interview questions and answers
jdbc interview questions with answers
jdbc sample code
JDBC Tutorial
jdbc type 1 driver
jdbc type 2 driver
jdbc type 3 driver
jdbc type 4 driver
Jdeveloper
JDK
JDK8
JEE Tutorial
jframe
jframe creation
jframe position
jframe positioning
JIRA
JMeter
JMS
JMX
join()
joining threads
JPA
JQuery
JS
JSF
JSF Tutorial
JSONP
JSP
jsp and java beans
jsp and servlets
jsp and xml
jsp api
jsp code
jsp compilation
jsp conversion
jsp directives
jsp error page
jsp error page directive
jsp implicit objects
jsp interview
jsp interview questions
jsp introduction
jsp intvw questions
jsp life
jsp life cycle
jsp life-cycle
jsp lifecycle
jsp page directive
jsp questions
jsp sample
jsp scripting
jsp scriptlets
jsp servlets
jsp summary
jsp synopsis
jsp tag libraries
jsp tag library
jsp taglib
jsp tags
jsp technology
jsp to servlet
jsp to servlet conversion
jsp translation
jsp usage
jsp usebean
jsp xml tags
jsp xml tags usage
jsp-servlet
jsp:getProperty
jsp:setProperty
jsp:usebean
jsps
JSTL
JUnit testing
keyword synchronized
keyword volatile
Keywords
Lambda Expressions
Learning
libraries
life cycle
life cycle of a jsp
life cycle of a servlet
life cycle of a thread
life cycle of jsp
life cycle of threads
lifecycle of a thread
linked list
linkedhashmap
linkedhashset
linkedlist
linux
List
listeners
lists
Literals
locale
lock manager pattern
lock scope
locking objects using threads
log
Logging
logging errors
logical and
logical operators
logical or
loops
loosely coupled
making an arraylist
making threads sleep
making threads sleep for time
MapReduce
maps
maps usage
Maven
Maven Tutorial
max priority
member access
method arguments
method local inner class
method overloading
method overriding
method return types
methods creating classes
min priority
Miscellaneous
mobile
mock exam
model view controller
model view controller design pattern
model view controller pattern
Multi Threading
Multi-threading
multiple threads
multiplication
multithreading
multithreading in java
multithreading interview questions
multithreading questions
mvc
mvc design pattern
mvc pattern
MyEclipse
mysql
nested java lock
nested java locks
nested java thread locks
nested locks
nested thread locks
NetBeans
Networking
new
news
nio
NonAccess Modifiers
norm priority
normal inner class
Normalization
not equal to
Notepad
notify
notifyall
number format
numberformat
numbers
object comparison
object notify
object orientation
object oriented
object oriented programming
Object Oriented Programming in java
objects interview questions
ocmjd certification
ocmjd certification eligibility
OO
OO Java
oops
OpenCSV
OpenCV
opening jsp tags
OpenJDK
OpenJFX
Operators
or
Oracle
Oracle ADF Mobile
Oracle Certified Exams
oracle certified master java developer
oracle database
ORM
other topics
out
overloading
overloading constructors
overloading in java
overriding
page
page directive
page scope
parsing
passing variables
passing variables to methods
performance
Platform
Playing with Numbers
points to remember
polymorphism
positioning a frame
post
practice exam
Primitive Casting
primitive variables
printwriter
priority queue
priority queues
priorityqueue
priorityqueues
private
processing form values
Products
programming
Projects
protected
public
put
questions
questions on garbage collection
questions on java strings
queue
quick recap
quick review
race conditions
read objects from stream
reading http request header
RealTime_Tips
redirecting to another servlet
redirection
reference
reference variable casting
reference variables
Refreshing Java
regex
Regular Expressions
regular inner class
relational operators
reminder
request
request dispatcher
request forwarding
request header
request object. httpservletrequest
request scope
requestdispatcher
response
RESTClient
RESTful
retrieving values from session
return error codes
return types
returning values
runnable
runnable interface
running
running java programs
RUP
sample jsp
sample questions
sample questions scwcd
sample servlet
scanner
Scene Builder
scjd certification
scjd certification eligibility requirements
scjp
SCJP Certification
scjp exam
scjp exam questions
scjp exam sample questions
scjp questions
scjp test
scjp test questions
scope
scope of java locks
scope of java thread locks
scope of locks
scripting in jsp
scriptlet tags
scriptlets
scriptlets in jsp pages
scwcd
scwcd certification
scwcd certification practice exam
scwcd exam
scwcd exam questions
scwcd jsp summary
scwcd mock exam
scwcd mock exam answers
scwcd practice exam
scwcd practice test
scwcd questions
scwcd test
SDLC
searching
searching arrays
searching collections
searching in java
searching treemap
searching treesets
security
self assement
self assement scwcd
self assessment scjp
self test
self test scjp
self test scwcd
send error method
senderror method
sending error code to browser
serialization
serialization in java
serialization interview questions
Serialization on Swing
serialization questions
service
service method
servlet
servlet and forms
servlet and jsp
servlet api
servlet attributes
servlet code
servlet container
servlet context
servlet error handling
servlet exception handling
servlet handling http request
servlet initialization
servlet initialization parameters
servlet interview
servlet interview questions
servlet interview questions with answers
servlet intvw questions
servlet life cycle
servlet lifecycle
servlet questions
servlet questions with answers
servlet request
servlet request dispatcher
servlet request type
servlet skeleton
servletcontext
servletcontextevent
servletrequest
Servlets
servlets and jsps
servlets api
servlets details
servlets request handling
session
session clean up
session event listeners
session facade pattern
session interview questions
session invalidation
session listeners
session management
session questions
session scope
session timeout
session tracking through url rewriting
set collections
set status method
setattribute
sets
setstatus method
setting bean property
setting request type
short circuit operators
Singleton
sleep
sleeping threads
soapUI
Software Installation
sorting
sorting arraylist
sorting arrays
sorting collections
special collections
special inner classes
split
spring
spring and hibernate interview questions
spring batch
Spring Core
Spring Framework
Spring Integration
spring interview questions
Spring JDBC
Spring MVC
Spring security
Spring tutorial
SQL
SQL and database tutorial examples
SQL Tutorial
SSL
stack
stacks
stacks and heaps
static
static class
static declaration
static imports
static inner
static inner class
static method
Static variable
stopped
stopping a thread
stopping thread
stopping threads
Stored Procedure
storing values in session
Streams
strictfp
StrictMath
string
string buffer
string builder
string class
string formatting
String Handling
string interview questions
string manupulation
string questions
string tokenizer
stringbuffer
stringbuffer questions
stringbuilder
Strings
strings in java
struts
Struts 1
Struts 1.2
Struts 2
struts framework interview questions
struts interview questions
struts interview questions with answers
struts mvc interview questions
struts questions
Struts2
StrutsBooks
submitting request
subtraction
Sun Certification
sun certified java developer
Sun Certified Java Programmer
swing
swing action performed
swing and colors
Swing Components
swing event handling
swing event listeners
swing events
Swing Hacks
swing images
Swing Look And Feels
swings
swings frame
switch block
switch case block
switch case statement
Sybase
Sybase and SQL Server
synchronization
synchronized code
synchronized keyword
synchronized method
System Properties
tag lib
tag library
tag-lib
taglibs
tags
TDD
Technical Blogging
ternary operator
Test Driven Development
test scjp
Testing
the context
the session
the volatile keyword
thread
thread class
thread deadlocks
thread interaction
thread interruption
thread life cycle
thread lifecycle
thread lock scope
thread locks
thread notify
thread priorities
thread race conditions race conditions in threads
thread sleep
thread states
thread stoppage
thread stopping
thread synchronization
thread syncing
thread yield
Threads
threads in java
threads interview questions
threads life cycle
threads questions
tibco
tightly coupled
tips
tips and tricks
tips.FXML
tokenizing
Tomcat
Tools
toString
transitions
treemap
treeset
tricks
Tricks Bag
try catch
try catch finally. finally block
Tutorial
type casting in java
ui programming with java swings
UML
unboxing
unit testing
unix
url rewriting
use bean
usebean
using a arraylist
using collections
using colors
using colours
using command line arguments
using different fonts
using expressions
using font
using fonts
using fonts in swings
using hashmap
using http session
using httpsession
using iterator
using java beans in jsp
using javabean in jsp
using javabeans in jsp
using javac
using lists
using maps
using request dispatcher
using scriptlets
using session persistense
using sets
using special fonts
using system properties
using the jsp use bean
using treeset
using use bean
Using Variables
using volatile
Using Wrappers
using xml in jsp
Util pack
value object
value object design pattern
value object pattern
var-args
varargs
Variable Arguments
Variables
vector
vector questions
vectors
visibility
vo pattern
volatile
volatile keyword
volatile variables
wait method
waiting
web app exception handling
web app interview
web application deployment
web application exceptions
web application scope
web application security
web component developer
web component developer certification
web context
web context interfaces
web context listeners
web interview questions
web security
web server
web servers
Web services
web.xml
web.xml deployment
webapp log
weblogic
website hacking
website security
what are threads
what is a java thread
what is a thread
what is thread
while loop
windows
windows 8
wrapper classes
wrappers
write objects to stream
WSAD
xml
xml and jsp
xml tags
xslt
yield()












